

It is a material that deforms when a weak force is applied at room temperature but restores to its original form when the external force is removed. The product once vulcanized cannot be reformed in the permeant form by applying heat and/or pressure.
The elastic substance that deforms when the external force is applied but restores to its original form when removed. A strong bond is generated between rubber molecules by applying sulfur or other cross linking agent on the raw material rubber.

| Type | Key Description |
|---|---|
| NATURAL RUBBER | - Resin of the Hevea brasiliensis rubber tree is 'tapped', that is, wounded to collect its sap and it is solidified to produce the rubber.
- It has been collected from the Amazon River since 1800 → Processing Method: Centrifugation and evaporation |
| SYNTHETIC RUBBER | - It is produced as a petroleum by-product and widely produced. - Type: SBR, EPDM, ECO, FKM etc. |
Nitrile Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
NBR |
| Chemical Structure | 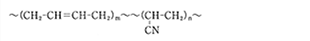 |
| Usage | Bearing seal, Encoder seal, Shock absorber seal |
Hydrogenated Nitrile Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
HNBR |
| Chemical Structure | 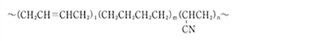 |
| Usage | Power steering seal |
Fluorine Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
FKM |
| Chemical Structure |  |
| Usage | Engine seal,Valve stem seal |
Acrylic Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
ACM |
| Chemical Structure |  |
| Usage | Transmission seal, O/D-Ring |
Ethylene-Propylene Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
EPDM |
| Chemical Structure | 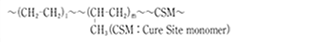 |
| Usage | O-RING, Gasket Brake用 CUP, Seal piston |
Silicon Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
VMQ |
| Chemical Structure |  |
| Usage | O-Ring, Gasket |
Fluorine Silicon Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
FVMQ |
| Chemical Structure |  |
| Usage | O-Ring, Gasket |
Chloroprene Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
CR |
| Chemical Structure |  |
| Usage | Seal, Boot |
Styrene-Butadiene Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
SBR |
| Chemical Structure | 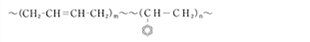 |
| Usage | Diaphragm |
Polyurethane Rubber
| Abbreviation (ASTM D 1418) |
AU |
| Chemical Structure | 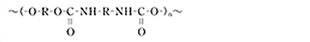 |
| Usage | Seal |